Constructors & its Types
{
}
{
System.out.println("Constructor created.");
}
class_name()
{
//display default values of members variable
}
MCA2()
{
System.out.println("Constructor created.");
System.out.println(rollno);
System.out.println(name);
}
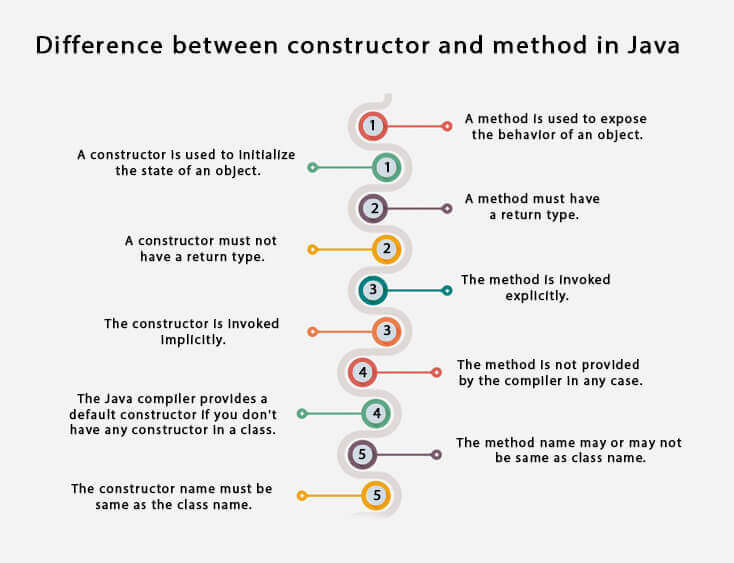
- In Java, a constructor is a block of codes similar to the method.
- It is called when an instance of the class is created.
- At the time of calling constructor, memory for the object is allocated in the memory.
- It is a special type of method which is used to initialize the object.
- Every time an object is created using the new() keyword, at least one constructor is called.
- It calls a default constructor if there is no constructor available in the class.
- In such case, Java compiler provides a default constructor by default.
- There are two types of constructors in Java:
- 1. No argument constructor or Default constructor
- 2. Arguments constructor
- Rules for creating Java constructor
- Constructor name must be the same as its class name.
- A Constructor must have no explicit return type.
- A Java constructor cannot be abstract, static, final, and synchronized.
- Java automatically created default constructor.
- It is automatically called when objects are created.
- Full Example:
- A constructor is called "Default Constructor" when it doesn't have any parameter.
- Syntax:
{
}
- Example:
{
System.out.println("Constructor created.");
}
- Full Example:
- The default constructor is used to provide the default values to the object like 0, null, etc., depending on the type.
- Syntax:
class_name()
{
//display default values of members variable
}
- Example:
MCA2()
{
System.out.println("Constructor created.");
System.out.println(rollno);
System.out.println(name);
}
- Full Example:
2.0 Arguments or Parameterized Constructor
- A constructor which has a specific number of parameters is called a parameterized constructor.
- Why?
- The parameterized constructor is used to provide different values to distinct objects.
- However, you can provide the same values also.
- Syntax:
class_name(agruments)
{
}
- Example:
MCA2(int rollno, String name)
{
System.out.println(rollno);
System.out.println(name);
}
How to pass arguments to constructors in main() method?
MCA2 r1 = new MCA2(101,"Sarthak");
3.0 Overloading Constructor
3.0 Overloading Constructor
- Constructors can also be overloaded.
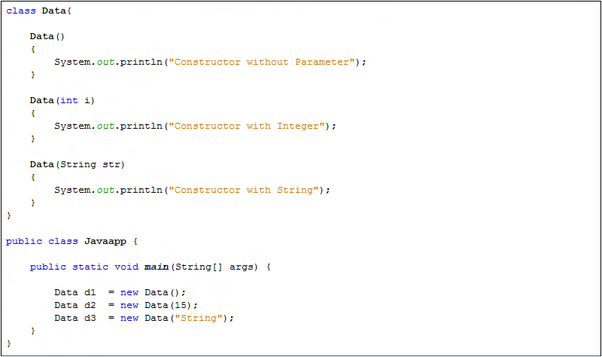
- Constructor overloading is a concept of having more than one constructor with different parameters list.
- Each constructor is calling according to its signature matching.
- For e.g. MCA2 class has 3 types of constructors.
- Full Example:
Tags:
Core java