Lesson Plan: Unit - 04
Subject: P15A2AAD - Android Application Development
Topic of Study: Using Build-in Layout Classes
Grade/Level: Master of Computer Applications
Objective: To draw and demonstration of different layout classes
Time Allotment: 55 Minutes
- Using Build-in Layout Classes
- Layouts are derived from android.view.ViewGroup
- The types of layouts built-in to the Android SDK framework include…
- FrameLayout
- LinearLayout
- RelativeLayout
- TableLayout
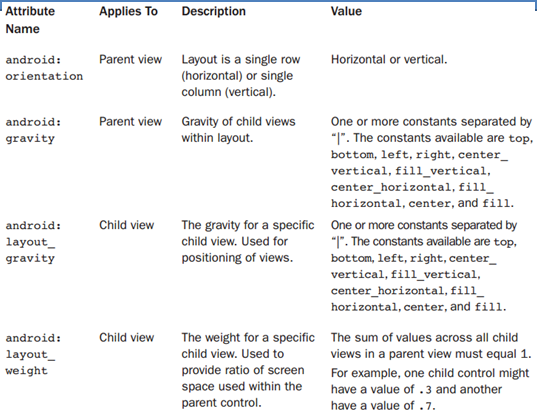
- Layout attributes apply to any child View within that layout.
- Syntax: android:layout_attribute_name=”value”
- You can find basic layout attributes in the ViewGroup.LayoutParams class.
- Some of the important attributes shared by all ViewGroup subtype.
- Exa. of Common Attributes:
- Using FrameLayout
- A FrameLayout view is designed to display a stack of child View items.
- You can add multiple views to this layout, but each View is drawn from the top-left corner of the layout.
- You can find the layout attributes available for FrameLayout child View objects in android.control.FrameLayout.LayoutParams.
- Exa.
- Using Linear Layout
- A LinearLayout view organizes its child View objects in a single row or column, depending on whether its orientation attribute is set to horizontal or vertical.
- This is a very handy layout method for creating forms.
- You can find the layout attributes available for LinearLayout child View objects in android.control.LinearLayout.LayoutParams
- Exa.
- Using Relative Layout
- The RelativeLayout view enables you to specify where the child view controls are in relation to each other.
- For instance, you can set a child View to be positioned “above” or “below” or “to the left of” or “to the right of” another View, referred to by its unique identifier.
- You can find the layout attributes available for RelativeLayout child View objects in android.control.RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.
- Exa.
- Using Table Layout
- A TableLayout view organizes children into rows.
- You add individual View objects within each row of the table using a TableRow layout View (which is basically a horizontally oriented LinearLayout) for each row of the table.
- Each column of the TableRow can contain one View (or layout with child View objects).
- You place View items added to a TableRow in columns in the order they are added.
- You can find the layout attributes available for TableLayout child View objects in android.control.TableLayout.LayoutParams.
- Exa.
- Using Absolute Layout
- The AbsoluteLayout class has been deprecated.
- AbsoluteLayout uses specific x and y coordinates for child view placement.
- This layout can be useful when pixel-perfect placement is required.
- However, it’s less flexible because it does not adapt well to other device configurations with different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Under most circumstances, other popular layout types such as FrameLayout and RelativeLayout suffice in place of AbsoluteLayout, so we encourage you to use these layouts instead when possible.