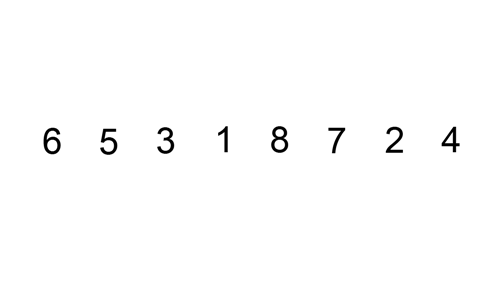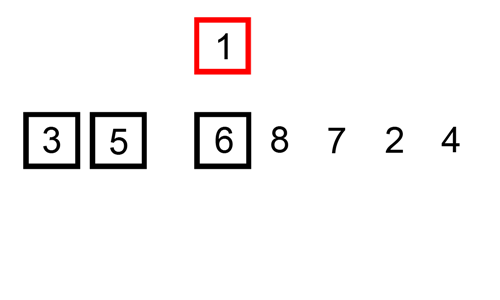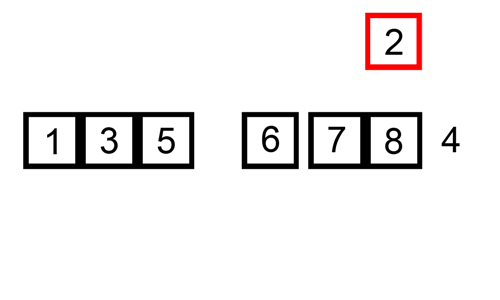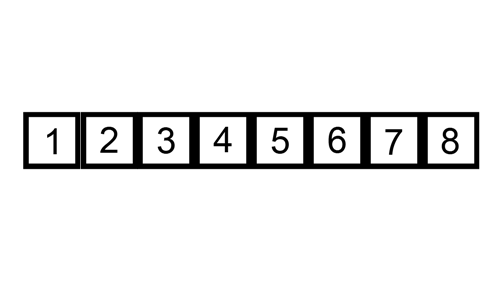Sorting in Collection
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("One");
al.add("Second");
al.add("Third");
al.add("Four");
Collections.sort(al);
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
Example to sort string objects in reverse order
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("One");
al.add("Second");
al.add("Third");
al.add("Four");
Collections.sort(al,Collections.reverseOrder());
Iterator i=al.iterator();
while(i.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(i.next());
}
Example to sort Wrapper class objects
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add(Integer.valueOf(201));
al.add(Integer.valueOf(101));
//internally will be converted into objects as Integer.valueOf(230)
al.add(230);
Collections.sort(al);
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
- Sorting is any process of arranging items systematically
- It has distinct meanings: ordering: arranging items in a sequence ordered by some criterion, categorizing: grouping items with similar properties.
- There are two types of sorting: Ascending and Descending.
- Types of Sorting Techniques
- Bubble Sort.
- Selection Sort.
- Merge Sort.
- Insertion Sort.
- Quick Sort.
- Heap Sort.
- We can sort the elements of:
- String objects
- Wrapper class objects
- Collections class provides static methods for sorting the elements of a collection.
- If collection elements are of a Set type, we can use TreeSet.
- Collections class provides methods for sorting the elements of List type elements.
- public void sort(List list): is used to sort the elements of List. List elements must be of the Comparable type.
ArrayList
al.add("One");
al.add("Second");
al.add("Third");
al.add("Four");
Collections.sort(al);
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
Example to sort string objects in reverse order
ArrayList
al.add("One");
al.add("Second");
al.add("Third");
al.add("Four");
Collections.sort(al,Collections.reverseOrder());
Iterator i=al.iterator();
while(i.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(i.next());
}
Example to sort Wrapper class objects
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add(Integer.valueOf(201));
al.add(Integer.valueOf(101));
//internally will be converted into objects as Integer.valueOf(230)
al.add(230);
Collections.sort(al);
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
Tags:
Java