Lesson Plan: Unit - 02 Microsoft Office
Subject: BELE2CFA: Computer Fundamentals And Applications
Topic of Study: Introduction to Excel's Parts, Workbook, Worksheet, Row, Column, Cell and Addressing Modes
Grade/Level: Bachelor of SCIENCE
Objective: To demonstrate and explain various options of Excel's Parts: Workbook, Worksheet, Row, Column, Cell and Addressing Modes in Microsoft Excel - 2010
14.0 Introduction to Excel 2010
- Excel is a collection of workbook program to organize, analyze and visualize the data through excel features.
- For Example:
- Charts
- Sorting
- Pivot Table
- Filtering
- 14.1 Parts of Excel - 2010
- A. Quick access toolbar
- B. Address of selected cell (For Example: A1)
- C. Formula bar
- D. Column name (For Example: A,B,...L, M...)
- E. Ribbon options
- F. Row name (For Example: 1,2,...15, 16...)
- G. Worksheet name (For Example: Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3...)
- H. Scrollbar
- I. Page View options
- J. Zoom options
14.0.1 Workbook
- A excel application files is called as Workbook.
- The default name of workbook in excel is Book1.
- The extension of excel is .xls / .xlsx
14.0.2 Worksheet
- A worksheet is an area where user can enter modify the data.
- A worksheet is collection of rows and columns.
- There are default 3 worksheets.
- The default name of these worksheets are Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3.
14.0.3 Row
- Row is an area which run in worksheet as horizontally.
- For Example: 1,2,3,4.....
- The name of first row is 1 and last row is 1048576.
14.0.4 Column
- Column is an area which run in worksheet as vertically.
- For Example: A, B, C, D....
- The name of first column is A and last column is XFD.
14.0.5 Cell
- The intersection part of row and column is called cell.
- It is always identify by Column and Row name,
- For Example: Column A and Row 1 then cell is A1
- The name of first cell is A1 and last cell is XFD1048576
14.0.6 Addressing modes
- Excel application are mostly used to manage different formula.
- A formula need address of cell, row or column of the current or other sheets.
- To write a formula we have different addressing modes.
- There are 3 types:
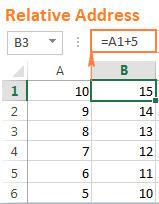
- Relative addressing modes
- It is standard technique to write a cell reference. (also called cell address)
- For Example:
- If cell A1 contains value 5, and cell B1 contains formula =A1+2. Then the formula B1 contains value 7.
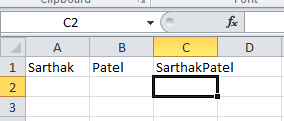
- If cell A1 contains value Sarthak, cell B1 contains value Patel and C1 contains =A1 & B1. Then the formula C1 contains value SarthakPatel.
- Absolute addressing modes
- It is another technique to write cell reference (also called cell address).
- It is use $ sign with each reference.
- For Example:
- If cell A1 contains value 5, and cell B1 contains formula =$A$1+2.
Then the formula B1 contains value 7.
- If cell A1 contains value Sarthak, cell B1 contains value Patel and C1 contains =$A$1 & $B$1. Then the formula C1 contains value SarthakPatel.
- Mixed addressing modes
- It is hybrid technique to write cell reference (also called cell address).
- It can write with absolute and/or relative address.
- For example, $A1 or A$1.